2. Listen to the following videos, click “continue” till finish, and reproduce, word to word or summary, the description for each video. (80 points)
2. BY Mike Andreasen
A. A database is a structured system for storing information and organize way. Its purpose is to provide an efficient way for people to find facts necessary to make a report or which can then be used for making decisions. Databases existed long before computers were even before computers were invented. File cabinets with file drawers and file folders with records written on a form that contained fields of information. Traditional computerized databases use the same basic hierarchal structure. The smallest component of a database is a field which contains a single value such as a name or number. A field has attributes that describe how to maybe what information it holds, what type of data information they contain for example if your last name may only allow a maximum of 20 letters, or the quantity purchase field may only on numbers 1 to 99. Other common data types including number fields, logical yes or no fields, or mental or comment fields. A record is a collection of fields that describe the entity such as a person, product or sales transaction. A collection of records of the same type form a data file directory layout must decide specifically which film will be included in each type of record. A record type for sales transactions will naturally contain different information than a record type for customers or products or concerts held in the arena. All of the data files, also called database files form the database itself. The resulting hierarchy can be compared to the files system structure, on a computer. Just as a folder on hard drive contains files which contain pages of information made up of words or information, so to the database files that are made up of records and fields that contain words and numbers.
B. Web databases can now provide nearly every person in the world access to information is made available to privileged few. Libraries have used scanners to digitize pages of rare books and atlases. Governments have made public records available so people who want to find their roots can find their birth, death and immigration records in databases all over the world. Television stations in many countries provide databases that contain audio and video of recent broadcasts. And schools and universities provide access to alumni directories. The websites are not limited to just simply displaying interesting information. Airlines, movie theaters and sports teams don't just publish their schedules and lists upcoming events, they also allow users to purchase and even print their own tickets online. you can also shop online for books, CDs, video, flowers, well the list is seemingly endless. And web databases are at the heart of all of it. With surprisingly similar database structures. Relational database are created with separate tables or products being offered for sale. Inventory in the warehouse, customer shipping information and billing information. If you decide to send your dad a cook book for Father's Day, you might choose dad's loves to cook in the product offered table. Once you confirm your order a current inventory table will be searched in a quantity in stock field will be decreased from 7 to 6. You will be asked to enter your dad's mailing address into the shipping address table. Then you will be asked to enter your own billing address and credit card information. Then you will enter your own address and of course your credit card information into the billing table.
C. A database can be classified according to the model used for its design. There are five common database models, flat file, relational, object-oriented, distributed and multimedia. This video will focus on the relational model. In relational database is an advanced version of basic database model. The traditional flat file database so-called because it contains only one file. That file consists of individual records comprised of fields of data. In relational database terminology. Databases files are called tables, records are called tuples and fields are called attributes. A disadvantage to a flat file database is that it consists of one file that contains records that must be searched in sequence. The process can be slow. The relational database on the other hand are made of several related files called tables. The information in each table is limited to one type of record. The customer table might contain only billing address and contact information. A product table might contain information related to inventory items such as manufacture, model, purchase cost, sales price, supplier and quantity in stock. An invoice table might only contain reference numbers and product numbers. The do we address the jobs would not appear in the invoice itself but the printed invoice would include a full billing address and then looked up in the customer table as the invoice had been created. In a well-designed relational database, the information is never entered a second or third time. Attributes are stored once and shared among the related tables. Any attribute that is changed in one table is automatically changed in all the other tables.
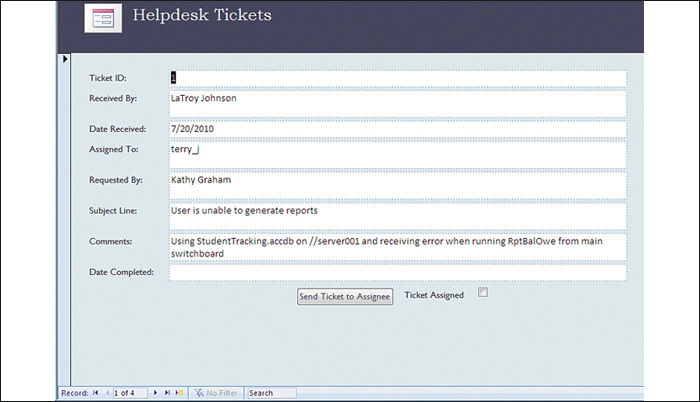
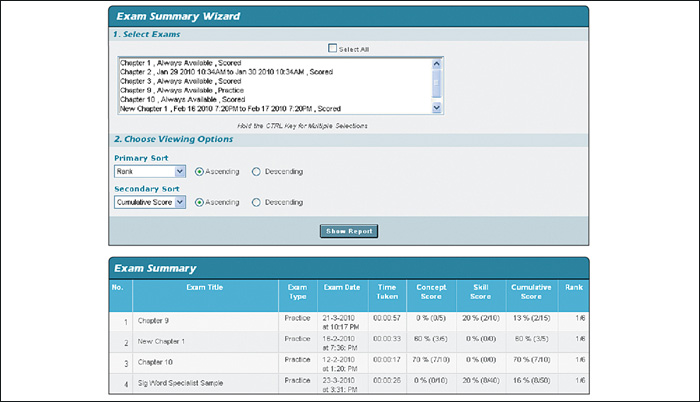
D. Why systems analyst designs a database, a methodology called the database management approach is used. The three basic steps in the design are creating a data structure, designing a user friendly interface and designing the searching and reporting features. As discussed in an earlier segment, creating the structure involves deciding which types of record are required and the size, quantity and types of fields each record should contain. The users who will be doing the data entry do not have to know anything about the inner workings of the database just as the driver does not need to know how an engine functions in order to drive it. But the input screen which is a part of the front-end must be easy to use and must not be confusing. Templates, forms are not only used as a convenient input method they can also detect and prevent data entry errors. For example all North American telephone numbers consistently three digit area code follows a seven digit subscriber number. Any entry containing letters or more or fewer than 10 digits can generate an error message and prompt the user to try again. Default responses can be preprogrammed to fill in input fields so that the data entry person can just press enter. When most customers or clients are from the same area for example the city and state names can be displayed by default. Perhaps the most important part of the database design is the setting up of the search and report features. The same templates created for data input and modification can also be used for records searches. By choosing query mode, entering a ZIP code, only those records with the matching code will be displayed. And a report can be created and printed from it. The report itself can be preformatted for a consistent appearance. More sophisticated data filters can be set up according to all sorts of criteria. The sales manager may want list of all customers from Boston who placed orders totaling more than $1 million last year. Of course the information can be a bit disappointing.
E. CRT or Cathode Ray Tube monitors work by using internal electron guns. There is one gun for each primary RGB color red green and blue. All three guns sweep the screen line by line, each striking red green or blue phosphors which coat the glass of the monitor. A shadow mask controls were each electron beam strikes the phosphors and is responsible for creating the pixel perfect. Once the combined beam has look across each line from top to bottom it begins again at the top. This is referred to as the refresh rate and occurs approximately 60 times or more a second on most monitors. The guns begin in the upper left corner of the screen sweep from left to right and then move down to the start of the next line. At the bottom right corner the beam moves diagonally to the upper left corner where it will begin again. Some adapters attempt to push the amount of lines that are perceived to be displayed by a process called interlacing. Interlacing involves scanning every other line giving the illusion has twice as many lines but usually giving a noticeable screen flicker as well.
F. The keyboard is a combination of electronic and mechanical device. When you press a key you close and electrical circuit on the circuit board underneath. This changes in the electrical pattern that is sent to the PC and the PC understands this change to mean that the key has been pressed. A variety of keyboard layouts are available each of the keys arranged differently their divorce for various languages for example and some English language keyboards at different layouts such as the favoric. Therefore the operating system must rely on a stored chart that helps them figure out which letter number or symbol to display a particular key is pressed. This chart is called the keyboard layout and you can load a different keyboard layout when you attach different keyboard to your PC.
G. As you move the PC mouse, the mouse ball on the underside of the device rotates in conjunction with the mouse service. As this happens two censors in the mouse pick up the movement, up and down or left and right and transmit the data to your PC.
H. T1 in addition to ISDN lines telephone companies sell leases for T carrier lines. A T-1 line carries 24 consecutive signals at the same time at a combined transfer rate of 1.544 Mb per second. T1 lines are widely used by businesses, educational institutions and to some Internet service providers. T3, a T-3 line is even more powerful than a T-1 line essentially equal to 28 T-1 lines. T-3 lines provide a combined transfer rate of 43 Mb per second. T-3 lines are used by very large organizations and telephone companies. T-3 lines also form the primary functions of the Internet. DSL a digital subscriber line, DSL uses a special DSL modem to transmit and receive digital signals for conventional twisted-pair cabling to the homes to the fiber-optic backbone of the Telephone Company. This service however is available to users only within 3 miles of the Telephone Company's central switching office. ADSL, asymmetrical digital subscriber line are popular form of DSL. ADSL offers high bandwidth services for faster download speeds when receiving data then when uploading or sending data.
a. Database Structure (10 points) |
b. Web Structure (10 points) |
c. Relational Database (10 points) |
d. DataBase Design (10 points) |
e. Super VGA CRT (10 points) |
f. Keyboard Layout (10 points) |
g. Mechanical Mouse (10 points) |
|
h. Communications Media (10 points) |
b. Answer the following question. [Refer to
pages 403-406 (10 points)
MicroSoft Access Relational Databases
A.
1. Data Type: Usually Numerical or Text (numbers and letters).
2. Name: Assigned by the person developing the database.
3. Size: The number of characters that can be entered.
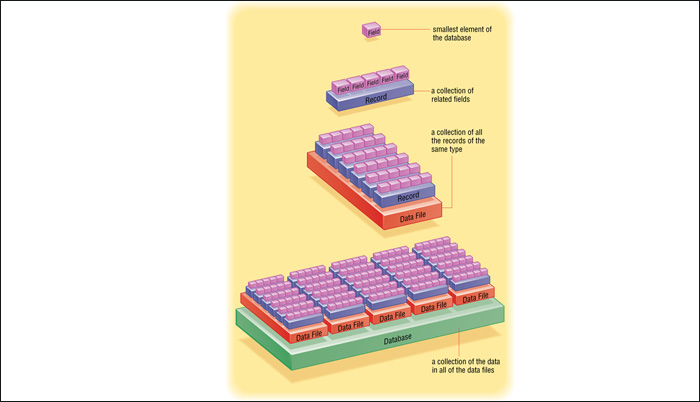
B. A Field is the smallest element in a database. A record is a collection of related fields. A Data File is a collection of all records of the same type. A Database is a collection of the data in all of the data files.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
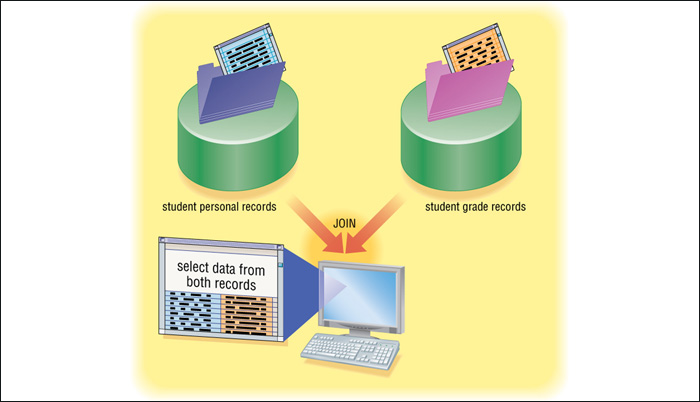
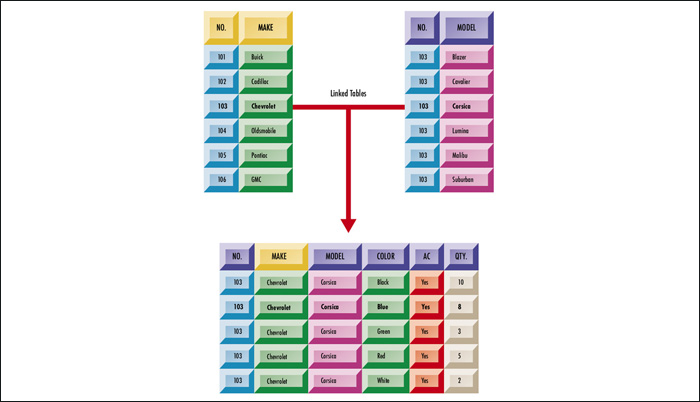
6. Describe, in your own words, what is a relational database and how the tables in the following figure relate to each other. [Refer to
page 415 on Relational Databases] (10 points)
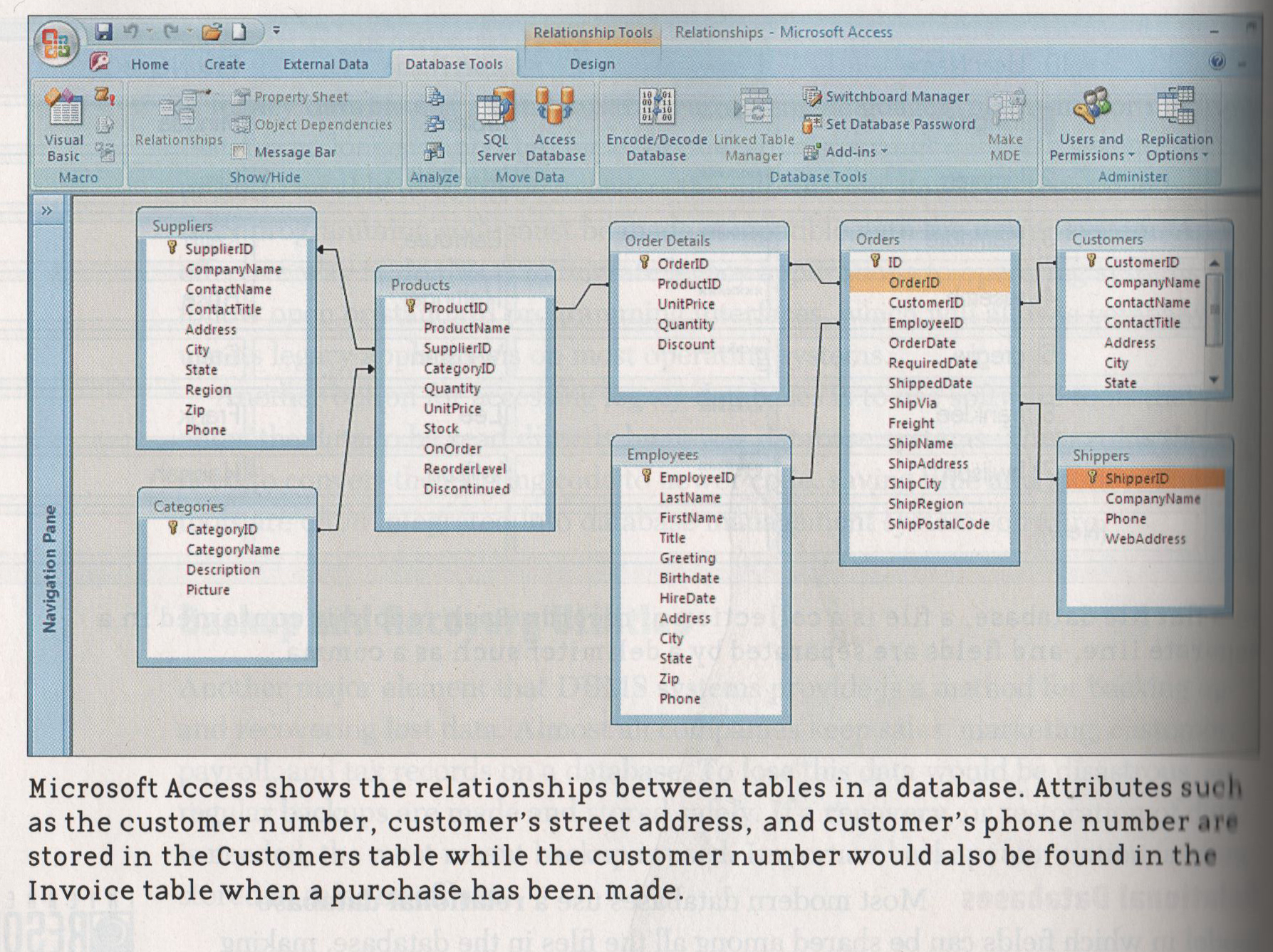
MicroSoft Access Relational Databases
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
7.Label the the following Drawing and describe what is the function of each. [Refer to
pages 410-414 (10 points)
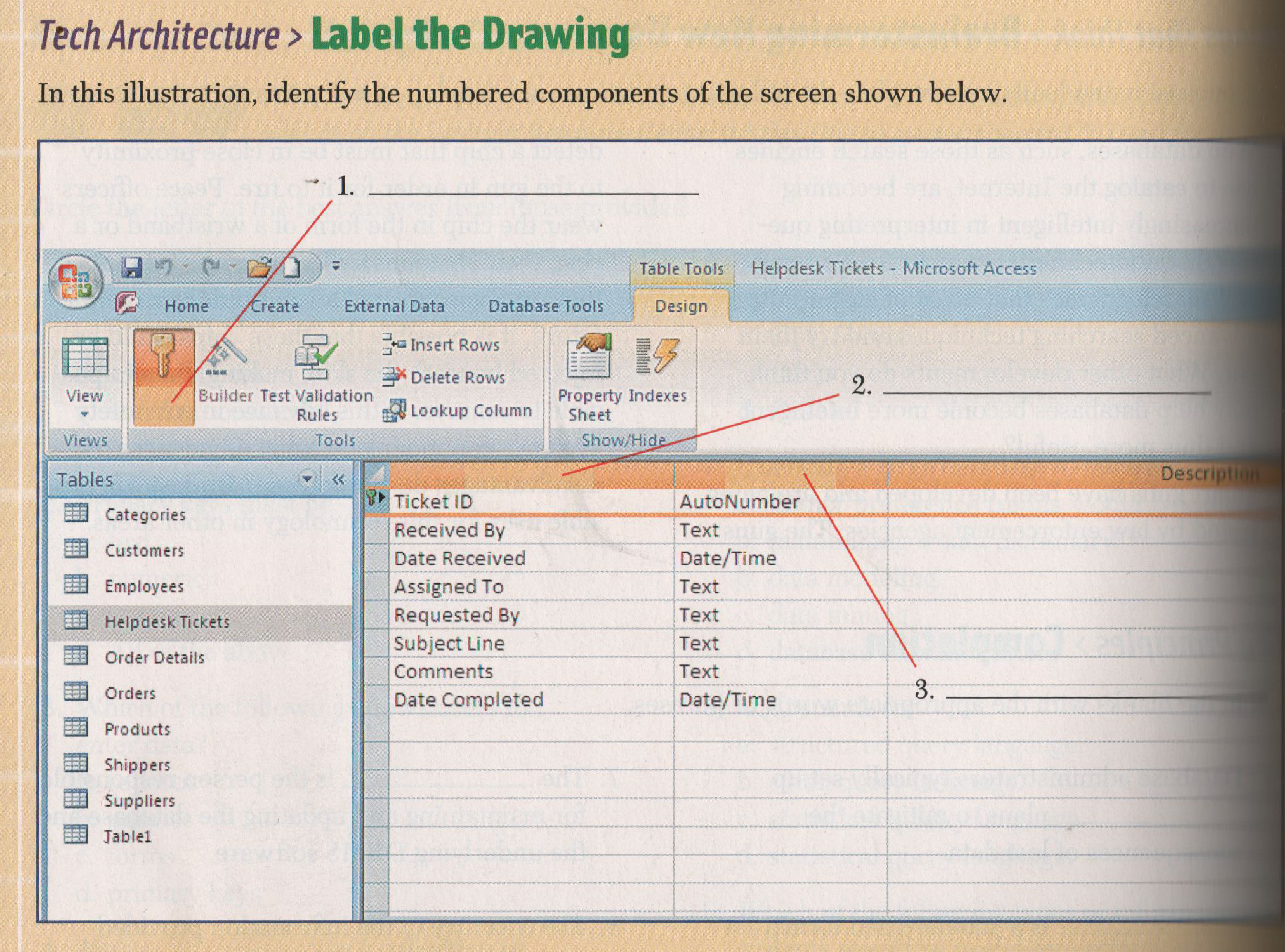
7. BY Mike Andreasen
1. Primary Key: is unique as to be able to locate a record quickly. First names are poor Primary Keys.
2. Field Name: A location into which one kind of information about an entity such as a name or address is entered.
3. Data type: Usually a number or letter.
1 - _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
8. Match the following network descriptions to each of their corresponding picture. [Write # against picture] (10 points)
|
|
[____9_Database File
|
|
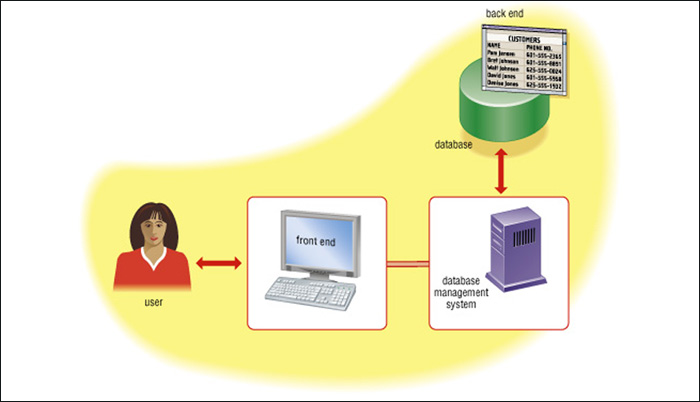
[____8_Database Response
|
|
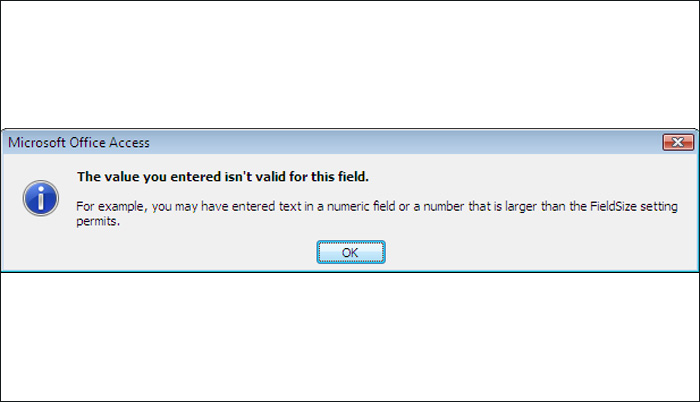
[____7_Data Validation___] |
|
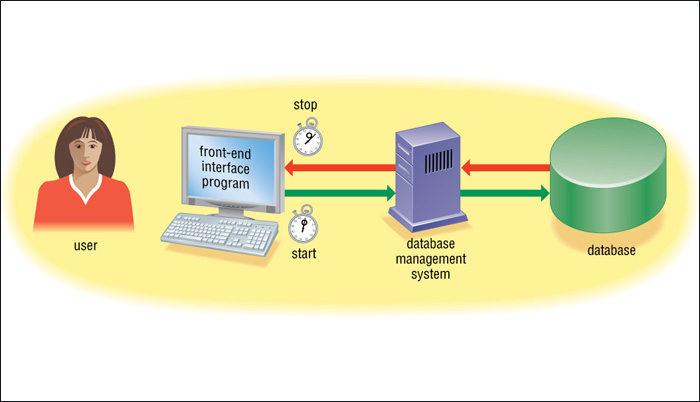
[____1_DBMS (Database Management System)
|
|
[___3_Microsoft Access____] |
|
[____6_FORM___] |
|
[__5_joining_____] |
|
[___10_Primary Key
|
|
[__4_Query____] |
|
[___1_Report
|